Tibialis Posterior Pain & Football
May 20 2008 | Articles
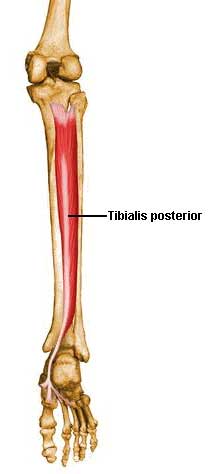
Tibialis Posterior Pain Explained
An injury prevalent in running activities, Tibialis Posterior pain can lead to Acquired Flat Feet and Foot Pain.
The severity of the injury may vary, with damage ranging from inflammation to partial or complete ruptures in the Tibialis Posterior tendon. As a result to the damage in the Tibialis Posterior tendon, the player will experience pain on the inside of his ankle, specifically in the area behind the bony prominence. Football players may acquire this condition as a result of a direct blow to their Tibialis Posterior Tendon.
The Tibialis Posterior Muscle originates from the back of the shin bones. As a tendon, the Tibialis Posterior Muscle runs the length of the inside of the ankle before it eventually reaches the middle of the foot, inserting itself into the tarsal bones.
Football players who regularly run on roads with tight bends or steep slopes may also develop this condition. Injuries of this kind do not manifest immediately but rather, they develop through time due to an overuse of the foot. With this condition, every step the player takes will put incredible strain on the tendon. Inflammation may soon follow, along with pain felt at the inside of the ankle.
This condition may be caused by Tibialis Posterior Dysfunction. Tibialis Posterior Dysfunction is basically flat feet or fallen arches.
Tibialis Posterior Pain Signs & Symptoms
Inflammation in the Tibialis Posterior Tendon and its surrounding sheath will make movement painful. Pain can especially be felt in movements that require pushing the foot downwards or turning it inwards. These movements are referred to as plantar flexion and inversion, respectively.
The Tibialis posterior may be sore to touch. However, the attachment of the tendon to the Navicular bone in the foot may also experience pain. The Navicular bone is located at the area where shoe laces are tied. The soreness typically originates from the medial malleolus, the bony prominence on the inside of the ankle. Sometimes, motion will cause this area to produce creaking sounds.
Podiatrists and Chartered physiotherapists can easily diagnose Tibialis Posterior Syndrome. However, they may need to convince the player that the pain is not really caused by the medial malleolus itself. An MRI scan will help eliminate the possibility of damage in the ankle joint and other bony structures within the foot.
Tibialis Posterior Pain Treatment
What you can do
Initially the ideal treatment must be guided with the P.R.I.C.E protocol: – protection, rest, ice, compression and elevation. However, ice must be applied with care since its direct contact with the skin can cause ice burns. The swelling within the Tibialis Posterior Sheath can be controlled and managed using this treatment. To relieve pain, reusable ice packs can be applied to the injury every two hours, for twenty minutes each time. Doctors may also prescribe Non Steroidal Anti Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs) in order to address the inflammation. Anti-inflammatory gels can also be used.

View Reusable ice packs
Doctors may recommend for the foot to be immobilised for a couple of weeks. In any case, the player must have a period of complete rest to allow the tendon to heal properly.
People who suffered from Tibialis Posterior Pain cannot simply go back to football after recovery. Podiatrist assessment must be conducted first since tendon problems usually result in abnormal mechanics in the lower leg. Common complications include over pronation in which the forefoot rolls over, causing the Tibialis Posterior Tendon to get overworked.
In some cases, the strain on the Tibialis Posterior may be attributed to ligaments which are unable to properly support the inside arch of the foot. Both of these conditions can be improved by using the
Dr Foot Sports Insoles.
By providing the inside arch with sufficient support, the Dr Foot Sports Insoles can reduce the strain on the Tibialis Posterior tendon.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() 5 Star Rating
5 Star Rating

View the Dr Foot Sports Insoles
Tibialis Posterior Pain Prevention
What you can do
Tibialis Posterior Pain can result from untimely participation in excessive physical activity. Physical activity must always increase gradually especially when starting or altering a fitness regime. For instance, when a footballer suddenly decides to run for 10 miles a day even though his usual routine calls for only 2 miles of running, he inevitably puts his body at risk. Such a danger can be prevented through the maintenance of a training log.
To reduce strain on the Tibialis Posterior, footballers must wear quality football shoes with shock absorbing insoles. Correction of conditions like flat feet and fallen arches may also prevent the development of Medial Tibial Stress Syndrome. With insertion of Orthotics into the footwear, pressure may be relieved from the Tibialis Posterior Tendon.
